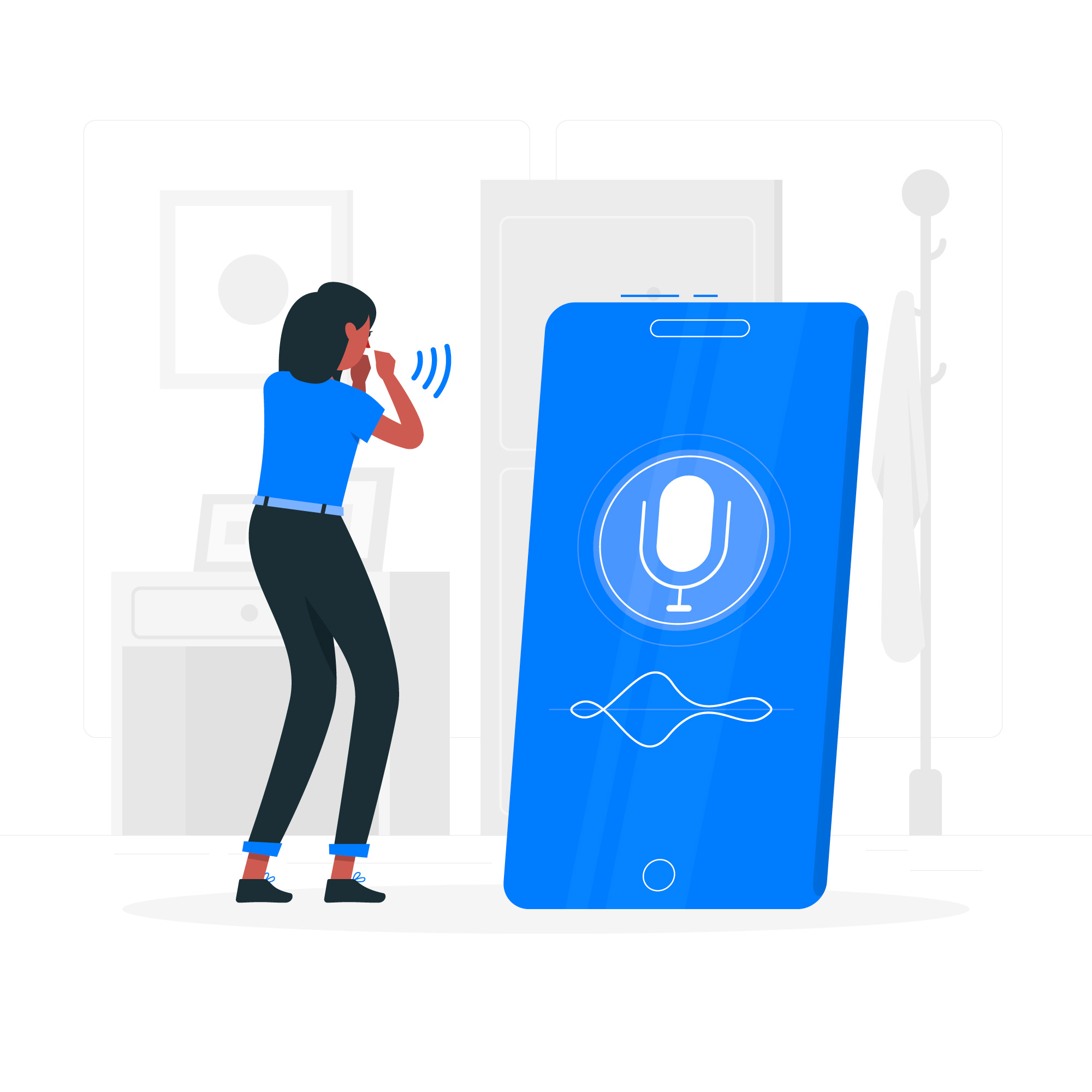
Voice User Interfaces (VUIs) and Touchless Interactions are two of the most exciting and rapidly developing technologies today. VUIs allow users to interact with devices and applications using voice commands, while touchless interactions allow users to interact with devices and applications without having to physically touch them.
VUIs and touchless interactions have a number of benefits over traditional input methods, such as keyboards and mice. Their natural and intuitive nature, combined with hands-free operation, makes them ideal for use in a variety of situations. For example, VUIs can be used to control smart home devices while driving, or to interact with wearable devices while exercising. Touchless interactions can be used to operate public kiosks without having to touch a shared surface, or to control video games without having to hold a controller.
VUIs and touchless interactions are still relatively new technologies, but they are already being used in a wide range of products and services. For example, VUIs are used in smart speakers, such as Amazon Echo and Google Home, and in virtual assistants, such as Siri and Alexa. Touchless interactions are used in smartphones and tablets, in video games, and in public kiosks.
As VUIs and touchless interactions continue to develop, they are likely to have a major impact on the way we interact with technology. They have the potential to make our lives easier and more convenient, and to open up new possibilities for interaction and design.
VUI and Touchless Interaction Statistics: What the Data Tells Us
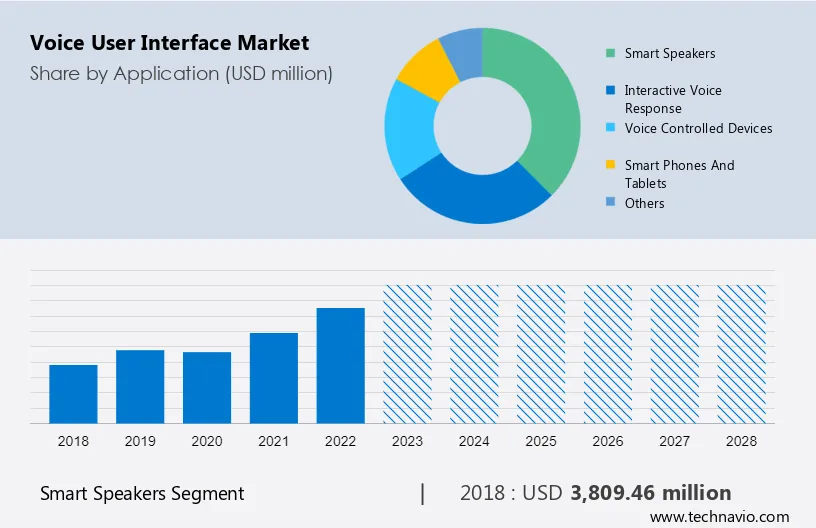
Source: Technavio
- The Voice User Interfaces (VUI) Market size is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 23.39% between 2023 and 2028. The market size is forecast to increase by USD 50,731.16 million.
- 77% of smart speaker owners use voice commands to control other smart devices in their homes.
- In 2022, 50% of smartphone users interacted with voice assistants on a daily basis.
- Touchless interactions are becoming increasingly popular in a variety of settings. For example, a recent study by Juniper Research found that the global touchless payment market is expected to reach $6.7 trillion by 2027.
How do VUIs and Touchless Interactions work?
Voice User Interfaces (VUIs)
VUIs use a combination of hardware and software to convert spoken language into text. The hardware component typically consists of a microphone and an audio processing unit. The software component consists of a speech recognition engine and a natural language processing (NLP) engine.
The speech recognition engine converts the audio signal from the microphone into a sequence of phonemes. Phonemes are the smallest units of sound that can distinguish one word from another. For example, the words “cat” and “hat” differ by only one phoneme (/k/ versus /h/).
The NLP engine then takes the sequence of phonemes and converts it into a sequence of words. This process is more complex than it sounds, as it requires the NLP engine to understand the context of the conversation in order to correctly identify the words that the user has spoken.
Once the NLP engine has identified the words, it can then take the appropriate action, such as launching an app, playing a song, or answering a question.
Touchless Interactions
Touchless interactions use a variety of sensors to detect user input without requiring them to physically touch the device. Some of the most common sensors used for touchless interactions include:
Cameras:
Cameras can be used to track the movement of the user’s body or hands. You can use this information to control a device or interact with a user interface.
Infrared sensors:
Infrared sensors can be used to detect the presence of the user’s hand in front of the device. You can use this information to control a device or interact with a user interface.
Ultrasonic sensors:
Ultrasonic sensors can be used to detect the distance between the user’s hand and the device. You can use this information to control a device or interact with a user interface.
Once the touchless interaction sensor has detected user input, it can then take the appropriate action. For example, a camera could be used to track the user’s hand movements to control a cursor on a screen. You can use an infrared sensor to detect when the user’s hand is in front of a device and turn on a light. You can use an ultrasonic sensor to detect the user’s hand’s proximity to the device and increase the music volume.
Designing VUIs and Touchless Interactions That People Will Love
Design for conversation
When designing a VUI or touchless interaction, it is important to keep in mind that users should feel like they are having a natural conversation with the system. This means using simple language, avoiding jargon, and understanding the context of the conversation.
For example, instead of saying “Please enter your name and address,” you could say “What is your name and address?” This makes the interaction more natural and engaging for the user.
Another way to make the conversation more natural is to use context-aware responses. For example, if the user asks “What is the weather like today?” you could respond with “It is sunny and 75 degrees in San Francisco, California today.” This is more informative and helpful than simply responding with “The weather is sunny.”
Be clear and concise
Users should be able to easily understand what the VUI or touchless interaction is doing and what they need to do next. This means providing clear instructions and feedback.
For example, instead of saying “Your request is being processed,” you could say “I am processing your request. Please wait a moment.” This provides the user with more information about what is happening and how long they need to wait.
Another way to be clear and concise is to use simple language and avoid jargon. For example, instead of saying “Please authenticate your account,” you could say “Please enter your username and password.” This is easier for the user to understand and follow.
Be consistent
The VUI or touchless interaction should behave consistently from one interaction to the next. This means using the same language and gestures, and providing predictable feedback.
For example, if the user asks “What is the weather like today?” you should always respond with the same information, such as “It is sunny and 75 degrees in San Francisco, California today.” If you sometimes respond with “The weather is sunny” and sometimes respond with “It is 75 degrees in San Francisco, California today,” this will be confusing for the user.
Another way to be consistent is to use the same language and gestures throughout the interaction. For example, if you start the interaction by saying “Hello, how can I help you today?” you should end the interaction by saying “Thank you for using our service. Goodbye.” This will make the interaction feel more polished and professional.
Be accessible
The VUI or touchless interaction should be accessible to all users, including people with disabilities. This means providing alternative ways to interact with the system, such as text-to-speech and speech-to-text.
For example, if a user is blind, they should be able to interact with the system using text-to-speech. This means that the system should be able to read the text on the screen to the user.
Another way to make the system accessible is to provide speech-to-text. This means that the system should be able to transcribe the user’s speech into text. This is helpful for users who are deaf or have difficulty speaking.
Test with users
It is important to test the VUI or touchless interaction with users early and often. This will help to identify any usability problems and make necessary changes before the system is deployed.
For example, you could test the system with a small group of users to get their feedback on the language, instructions, and feedback. You could also test the system with a larger group of users to see how they perform tasks using the VUI or touchless interaction.
By following these best practices, you can design VUIs and touchless interactions that are easy to use, efficient, and enjoyable for everyone.
Pros and Cons of VUIs and Touchless Technology
Benefits
Convenience:
VUIs and touchless interactions can be more convenient for users because they allow them to interact with devices and applications without having to use their hands or eyes. This can be useful in situations where the user’s hands are full, they are in a difficult-to-reach place, or they are unable to see.
For example, a user could use a VUI to control their smart home devices while they are cooking or to turn on a light switch while they are carrying groceries. A user could also use a touchless interaction to open a door without having to touch the doorknob or to flush a toilet without having to touch the handle.Accessibility:
VUIs and touchless interactions can make devices and applications more accessible to people with disabilities. For example, a blind person could use a VUI to interact with their phone or computer, and a person with limited mobility could use a touchless interaction to control their TV or thermostat.Efficiency:
VUIs and touchless interactions can help users to be more efficient in their tasks. For example, a user could use a VUI to set a timer while they are cooking or to send a message while they are driving. A user could also use a touchless interaction to turn on a light switch as they enter a room or to pause a video as they walk away from the TV.Safety:
VUIs and touchless interactions can improve safety in certain situations. For example, a user could use a VUI to control their car’s entertainment system without having to take their hands off the wheel. A user could also use a touchless interaction to open a door in a public restroom without having to touch the door handle.
Challenges
Accuracy:
VUIs and touchless interactions can be inaccurate, especially in noisy environments. This happens because VUIs depend on speech recognition technology, which background noise can affect. Touchless interactions can also be inaccurate if the user is not in the correct position or if the sensor is not calibrated properly.
Privacy:
VUIs and touchless interactions can collect a lot of data about users, which raises privacy concerns. For example, a VUI may collect data about the user’s voice, location, and interests. A touchless interaction sensor may also collect data about the user’s movements and interactions with the environment.
Cost:
VUIs and touchless interfaces can be expensive to develop and deploy. This can make it difficult for small businesses and startups to adopt these technologies.
Overall, VUIs and touchless interactions have the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with technology. However, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed before these technologies can be widely adopted.
Case studies of successful VUIs and touchless interactions
Amazon Alexa
Amazon Alexa is a voice user interface (VUI) that allows users to control their smart home devices, play music, get information, and more. Alexa is available on a variety of devices, including Amazon Echo smart speakers, Amazon Fire TV streaming devices, and Amazon Fire tablets.
Alexa works by using speech recognition technology to convert the user’s spoken words into text. This text is then processed by Alexa’s natural language processing (NLP) engine, which interprets the user’s intent. Once the NLP engine has interpreted the user’s intent, it can then take the appropriate action, such as controlling a smart home device, playing a song, or providing information.
For example, a user could say “Alexa, turn on the lights in the living room” to control their smart home lights. Or, they could say “Alexa, play my favorite song” to play their favorite song from their music library. Alexa can also be used to get information, such as the weather forecast or the score of a game.
Google Assistant
Google Assistant is another popular VUI. It is available on Android smartphones and tablets, as well as on a variety of other devices, such as Google Nest smart speakers and Google Home smart speakers. Google Assistant can be used to control smart home devices, play music, get information, and more.
Google Assistant works in a similar way to Alexa. It uses speech recognition technology to convert the user’s spoken words into text, and then it uses NLP to interpret the user’s intent. Once it has interpreted the user’s intent, it can then take the appropriate action.
Apple Siri
Apple Siri is a VUI that is available on iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch devices.You can use Siri to control smart home devices, play music, get information, and more.
Siri works in a similar way to Alexa and Google Assistant. It uses speech recognition technology to convert the user’s spoken words into text, and then it uses NLP to interpret the user’s intent. Once it has interpreted the user’s intent, it can then take the appropriate action.
Amazon Go
Amazon Go is a chain of convenience stores that use touchless interactions to allow customers to check out without having to go through a traditional checkout lane. Customers simply scan their Amazon Go app as they enter the store, and then they can pick up the items they want and walk out. The app will automatically charge the customer’s account for the items they have purchased.
Amazon Go uses a variety of sensors, including cameras and weight sensors, to track the items that customers pick up and put back. Businesses use this information to automatically charge the customer’s account for the items they have purchased.
Tesla Autopilot
Tesla Autopilot is a driver assistance system that uses touchless interactions to allow drivers to control their Tesla vehicles hands-free. You can use Autopilot to accelerate, brake, and steer the vehicle. You can use it to change lanes and navigate to destinations.
Tesla Autopilot uses a variety of sensors, including cameras, radar, and ultrasonic sensors, to collect information about the vehicle’s surroundings. Using this information, the vehicle is controlled and obstacles are avoided.
These are just a few examples of VUIs and touchless interactions. As these technologies continue to develop, we can expect to see them adopted in even more ways in the future.
To Conclude: The Main Insights
VUIs and touchless interactions are two of the most exciting and rapidly developing technologies today. They have the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with technology, making it more accessible, efficient, and enjoyable for everyone.
As these technologies continue to develop, we can expect to see them adopted in even more ways in the future. VUIs and touchless interactions can be used to control our homes, cars, workplaces, and healthcare. They can also be used to create new and innovative educational, entertainment, and customer service experiences.
At GeekyAnts, we are committed to helping our customers stay ahead of the curve by adopting the latest technologies. We have a team of experienced and talented engineers who can help you design, develop, and implement VUI and touchless interaction solutions for your business.
If you are interested in learning more about how VUIs and touchless interactions can benefit your business, please contact us today. We would be happy to discuss your specific needs and help you develop a solution that meets your requirements.