The internet is a powerful tool that can be used to access information, learn new things, and connect with others. However, for people with disabilities, the internet can be a barrier to opportunity. This is because many websites and web applications are not accessible to people with disabilities.
Web app accessibility is the practice of designing and developing web applications that can be used by people with a wide range of disabilities, including visual disabilities, hearing disabilities, cognitive disabilities, and mobility disabilities.
There are a number of benefits to making web apps accessible. First, accessibility is important for ensuring that people with disabilities have equal access to information and opportunities. Second, accessibility can improve the user experience for all users, including able-bodied users. For example, alt text for images can make it easier for everyone to understand the content of a web page, even if they cannot see the images.
In this blog post, we will discuss the importance of web app accessibility for US users and provide tips on how to make web apps more accessible.
Web App Accessibility Explained
Web app accessibility, in the context of the United States, refers to the practice of designing and developing web applications in a way that ensures they are usable and navigable by individuals with disabilities. It involves making digital content, such as websites and web-based tools, inclusive and accessible to all, regardless of their physical or cognitive impairments.
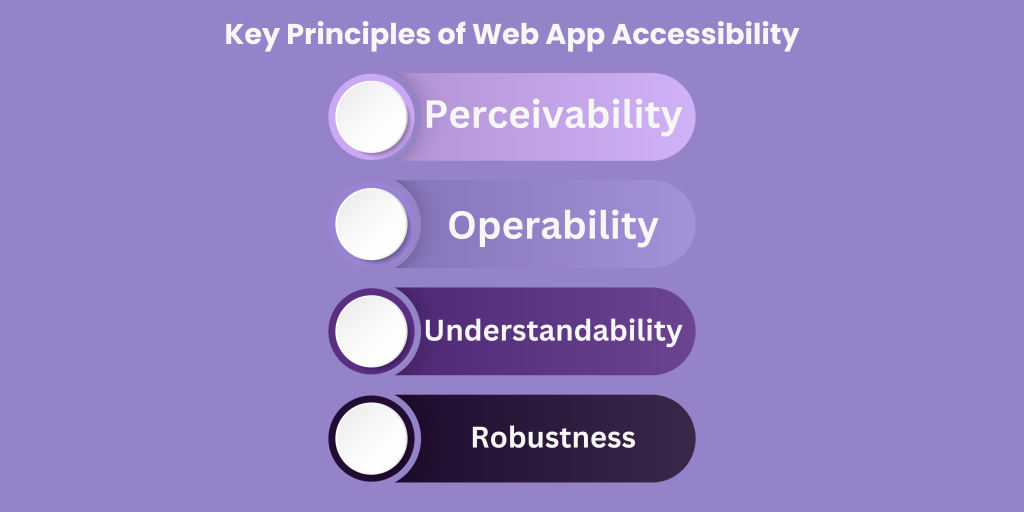
The key principles of web app accessibility include:
Perceivability:
Information and user interface components must be presented in a way that users can perceive, regardless of their abilities. This involves providing alternative text for images, captions for videos, and ensuring that text has sufficient contrast against the background for easy reading.
Operability:
Web apps should be operable through a variety of input methods, including keyboard navigation, voice commands, and assistive technologies like screen readers. This ensures that users with motor disabilities or those who cannot use a mouse can still interact with the application.
Understandability:
Content and navigation within the web app should be clear and straightforward. Users should be able to predict how the app behaves, and error messages should be easy to understand and correct. This benefits users with cognitive disabilities.
Robustness:
Web apps should be designed to be compatible with a wide range of assistive technologies and web browsers. This ensures that individuals with disabilities can access the content without encountering compatibility issues.
Web app accessibility is crucial for several reasons:
Legal Requirements:
In the United States, laws such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act require that federal agencies and organizations that receive federal funding ensure their digital content is accessible.
Inclusivity:
Accessible web apps promote inclusivity and allow individuals with disabilities to participate fully in online activities, from education to e-commerce.
Market Reach:
By making your web app accessible, you expand your potential user base to include people with disabilities, a substantial portion of the population.
Ethical Responsibility:
Ensuring web app accessibility is seen as an ethical responsibility, as it provides equal opportunities for all users to access information and services online.
Creating Accessible Online Experiences
Web accessibility standards are like a set of best practices for designing websites and digital apps to be user-friendly for everyone, regardless of their abilities. Think of them as a set of guidelines that website creators follow to ensure that their online content is welcoming and easy to use for a diverse audience.
The most important standard to know about is the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). These guidelines offer a comprehensive set of instructions, almost like a manual, for creating websites that are easy to navigate. They cover things like using clear text and images, making sure buttons and links can be easily clicked, and even providing alternatives for non-text content like images and videos. It’s kind of like a recipe book for making websites that are accessible to as many people as possible.
Web accessibility standards matter because they ensure that websites and digital tools are designed to be fair and helpful to everyone. Imagine a library where all the books are organized neatly, with clear labels, making it easy for everyone to find what they need. Web accessibility standards aim to make the online world just as welcoming and useful for people in the United States, no matter their abilities. It’s about creating an online space where everyone feels comfortable and included.
Web app accessibility checklist
Inclusivity and ensuring that everyone, regardless of their abilities, can access and use web applications with ease. To achieve this goal, we’ve compiled a list of the top 10 most important web accessibility practices. These practices serve as a comprehensive guide for developers and designers looking to create web apps that provide a welcoming and user-friendly experience for a U.S. audience.
Semantic HTML
- Properly nest elements to reflect their hierarchy on the page, making it easier for screen readers to interpret.
- Use appropriate HTML elements like <h1>, <nav>, <ul>, and <button> to structure your content logically.
Alt Text for Images
- Include descriptive alternative text (alt text) for images that explains their content or purpose.
- For decorative images, use empty alt attributes (alt=””) to let screen readers know the image is purely decorative.
Keyboard Navigation
- Ensure that all interactive elements, such as links, buttons, and form fields, can be accessed and used with the keyboard alone.
- Pay attention to the tab order to maintain a logical and consistent flow.
Descriptive Links and Buttons
- Use clear and concise text for links and buttons that conveys their function or destination.
- Avoid generic labels like “click here” or “read more,” which can be confusing for screen reader users.
Focus Styles
- Implement visible and distinctive focus styles for links, buttons, and form elements to help users understand where they are on the page.
- Ensure that focus styles do not compromise the overall design or readability.
Contrast and Color
- Maintain sufficient contrast between text and background colors to ensure readability for users with low vision or color blindness.
- Test your color choices using tools that check for contrast ratios to meet accessibility standards.
Testing with Assistive Technologies
- Regularly test your web app using screen readers, voice recognition software, and other assistive technologies.
- Ensure that your app functions as expected and that information is conveyed accurately.
Video and Audio Accessibility
- Provide captions or subtitles for videos to make spoken content accessible to individuals with hearing impairments.
- Offer transcripts for audio content so that all users can access the information.
Forms and Labels
- Associate labels with form fields using the <label> element and the for attribute.
- Ensure that error messages are clear and specific, assisting users in identifying and rectifying errors in forms.
Accessible Rich Internet Applications (ARIA)
- Use ARIA attributes when necessary to enhance accessibility, especially in dynamic web applications.
- Be cautious not to overuse ARIA, as misused attributes can create confusion for assistive technology users.
The benefits of accessible web apps for businesses
There are many benefits to making web apps accessible for businesses.By making web apps accessible, businesses can also improve their search engine rankings, reach new markets, and comply with international accessibility standards.These are some of the benefits:
Expanded Customer Base:
By making your web app accessible, you open the doors to a broader customer base. Approximately one in four adults in the U.S. has a disability, and catering to their needs can attract more users and potential customers.Legal Compliance:
Ensuring web app accessibility helps your business adhere to legal requirements, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Compliance can prevent costly legal disputes and fines.Improved Reputation:
Demonstrating a commitment to accessibility fosters a positive brand image. Customers and clients often view businesses that prioritize inclusivity more favorably.Competitive Advantage:
Accessibility can set your business apart from competitors. It can be a unique selling point, particularly in industries where accessibility is not yet a standard practice.Enhanced SEO:
Many accessibility practices, such as using descriptive alt text for images and creating semantic HTML, also improve search engine optimization (SEO). This can boost your web app’s visibility in search results.Increased User Engagement:
An accessible web app is more user-friendly for everyone, not just those with disabilities. This can lead to higher user satisfaction, longer session durations, and increased engagement.Better Mobile Experience:
Accessibility improvements often result in a more responsive and mobile-friendly web app. Given the prevalence of mobile device usage, this can attract and retain mobile users.Market Growth Potential:
As the population ages, the demand for accessible web apps will likely increase. Investing in accessibility now can position your business for future growth.Corporate Social Responsibility:
Embracing accessibility aligns with corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives, showcasing your commitment to social and ethical values.Reduced Maintenance Costs:
Fixing accessibility issues early in the development process can be more cost-effective than retrofitting later, saving both time and resources.
Web app accessibility checklist
Inclusivity and ensuring that everyone, regardless of their abilities, can access and use web applications with ease. To achieve this goal, we’ve compiled a list of the top 10 most important web accessibility practices. These practices serve as a comprehensive guide for developers and designers looking to create web apps that provide a welcoming and user-friendly experience for a U.S. audience.
- Netflix is a streaming service that provides video content to millions of users around the world. Netflix is committed to making its content accessible to everyone, including people with disabilities.
- In 2014, Netflix began providing transcripts for all of its videos. Transcripts are text versions of video content that can be read by people with hearing disabilities. Netflix also allows users to control the size of subtitles. Subtitles are text versions of video content that appear on the screen.
- In 2016, Netflix began providing audio descriptions for all of its original programming. Audio descriptions are narrated descriptions of the visual content of a video. Audio descriptions are helpful for people with visual impairments.
- Netflix has also made its website and mobile app more accessible. For example, Netflix provides alt text for all of the images on its website and mobile app. Alt text is a brief description of an image that is read by screen readers. Screen readers are assistive devices that read text aloud to people with visual impairments.
- Netflix’s commitment to accessibility has made its video content more accessible to millions of people around the world. Netflix is an example of how companies can make their products and services more accessible to people with disabilities.
- Captions and subtitles: YouTube provides captions and subtitles for all of its videos. Captions are text versions of the audio content of a video, while subtitles are text translations of the audio content of a video. Captions and subtitles are helpful for people with hearing impairments and people who are deaf.
- Audio descriptions: YouTube provides audio descriptions for many of its videos. Audio descriptions are narrated descriptions of the visual content of a video. Audio descriptions are helpful for people with visual impairments.
- Keyboard-only navigation: YouTube can be controlled using only a keyboard. This is important for people with mobility impairments who cannot use a mouse or touchpad.
- Simple language and clear navigation: YouTube uses simple language and clear navigation on its website and mobile app. This makes YouTube easier for people with cognitive disabilities to use.
- Adjustable playback speed: Spotify allows users to adjust the playback speed of music and podcasts. This can be helpful for people with learning disabilities or cognitive impairments who need to listen to content at a slower pace.
- Adjustable audio quality: Spotify allows users to adjust the audio quality of music and podcasts. This can be helpful for people with hearing impairments who need to listen to content at a higher volume or with reduced background noise.
- Sleep timer: Spotify has a sleep timer that allows users to set a time for the app to automatically turn off. This can be helpful for people who fall asleep while listening to music or podcasts.
- Lyrics: Spotify provides alt text for lyrics, which means that screen readers can read the lyrics to people who are blind or have low vision. Spotify also allows users to change the font size and color of lyrics, which can make them easier to read for people with visual impairments. Additionally, Spotify provides a lyrics widget for the Spotify web player, which allows users to view the lyrics to a song while they are listening to it. This can be helpful for people who are deaf or hard of hearing, as they can follow along with the lyrics and understand the song even if they cannot hear it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, web app accessibility is not just a legal obligation; it’s a gateway to a more inclusive, user-friendly, and socially responsible digital world. By prioritizing accessibility, businesses in the United States can tap into a wider customer base, bolster their reputation, and stay ahead of the competition. It’s a commitment that not only benefits your users but also your bottom line.
At GeekyAnts, we’re passionate about crafting accessible web solutions that empower businesses to thrive in the digital landscape. If you’re looking to enhance the accessibility of your web app or have any questions about our services, don’t hesitate to reach out to us. Together, we can make the web a more inclusive place for all. You can contact us here.
Let’s work together to create a more accessible and welcoming online experience for everyone.